Stem morphology and vascular anatomy of Fagopyrum esculentum Moench. under retardant chlormequat chloride action
Abstract
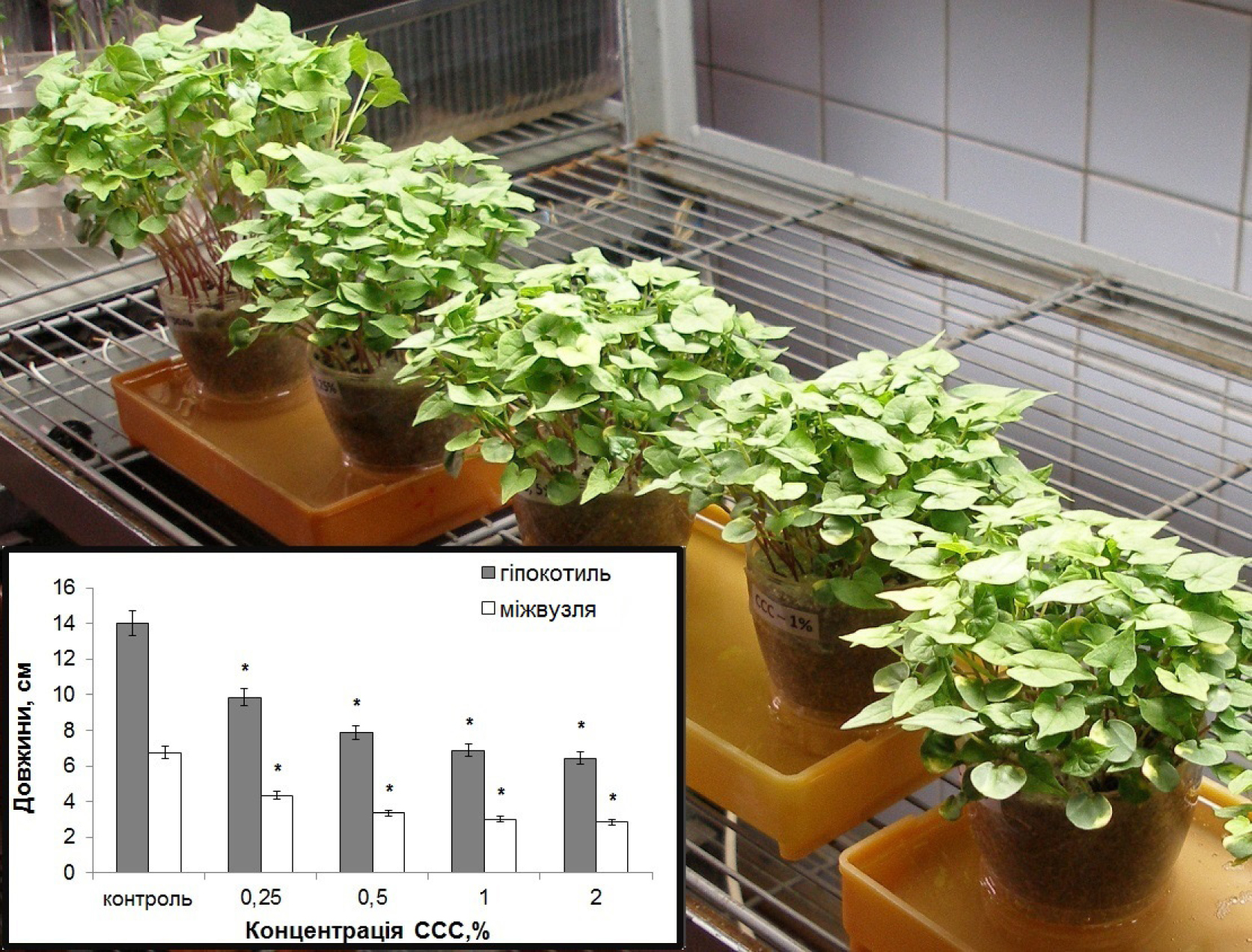
Effects of different concentrations of retardant chlormequat chloride on hypocotyl and first internode lengths of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.) were investigated. It was established that treatment of buckwheat plants with chlormequat chloride before presowing led to: reduction of stem length, activation of early and intensive lignification of vascular and mechanical elements, increasing number and size of vascular bundles in correlation with functional reconstructions on donor-acceptor connections of plant organs.
References
Степанюк Г.Я. 2010. Изменчивость анатомических признаков стебля ячменя (Hordeum vulgare L.) в условиях лесостепи Кемеровской области. Автореф. дис. … канд. биол. наук. Кемерово.
Bennett J.T., Virgona J.M., Martin P.J., O’Connell P. 2012. Effects of plant growth regulators that reduce stem height on yield of wheat in southern Australia. Materials of 16th Australian Agronomy Conference: 56–59.
Kuznetsov E.D., Vasilenko V.F., Kreslavski V.D. 1992. Stimulation effects of short-time red light and plant growth retardant on greening and formation of photosynthetic apparatus in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 30: 559–564.
Michalak A. 2006. Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 15 (4): 523–530.
North J.J., Laubscher C.P., Ndakidemi P.A. 2010. Effect of the growth retardant Cycocel® in controlling the growth of Dombeya burgessiae. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 9 (29): 4529–4533.
Tabatabaei S.S.M., Akhgari H. 2014. The investigation of growth reducer Cycocel effect on yield and some quantitative characteristics of rice (Oryza sativa) at different nitrogen kevels. Int. J. Farm. Allied Sci. 3 (2): 197–202.
Vermerris W., Nicholson R. 2006. Phenolic compound biochemistry. Springer Science + Business Media V.B.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.