The effect of fertilization with different rates of potassium and calcium carbonate on yield, vitamin C content, and salt concentration in the medium of stalk celery
Abstract
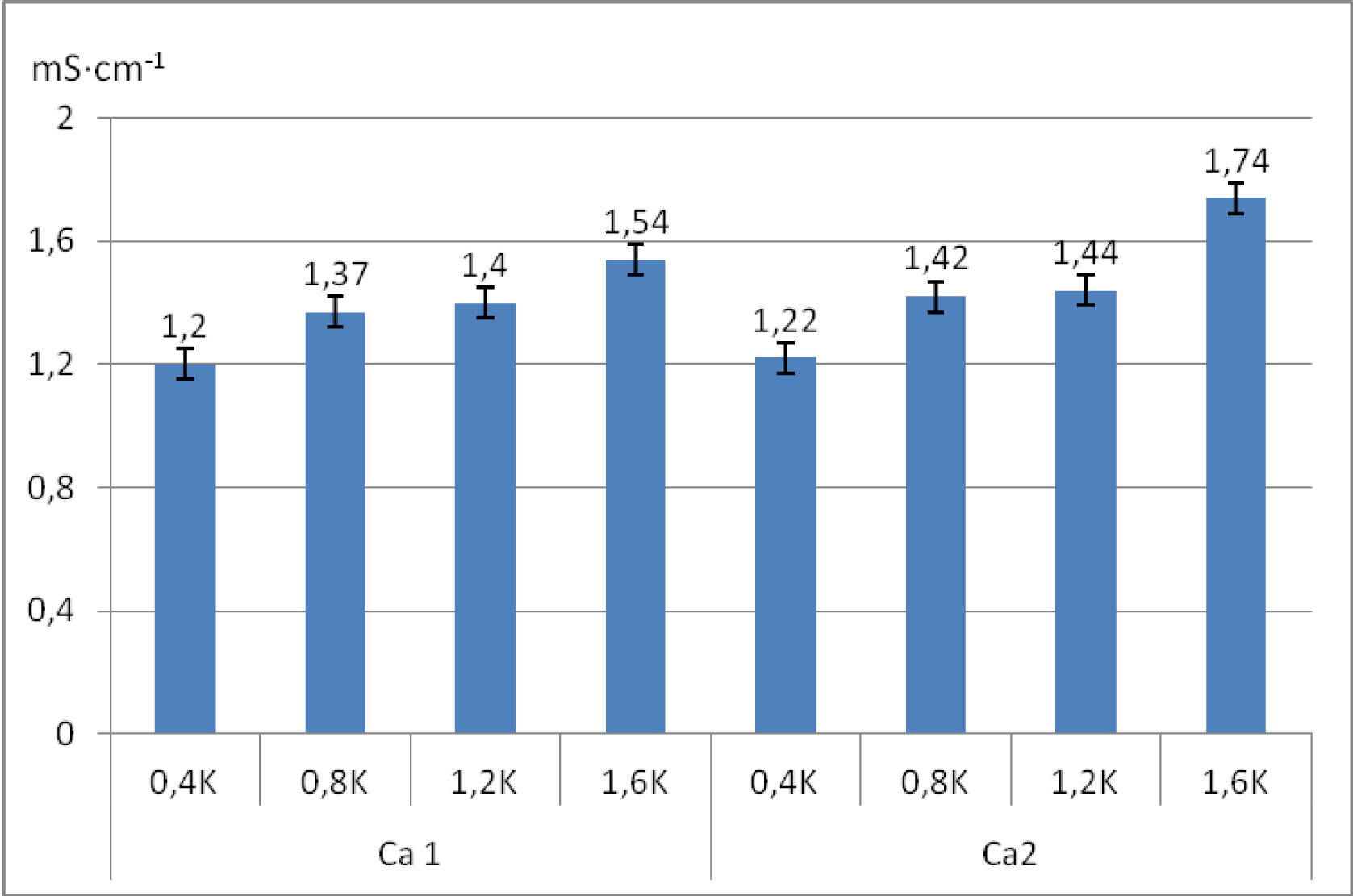
The effect of different rates of potassium: 0.4; 0.8; 1.2; 1.6 g K ∙ dm-3, and calcium carbonate: 5 g and 15 g CaCO3 ∙ dm-3, on stalk celery yield and vitamin C content as well as on salt concentration in the medium was analysed in a greenhouse experiment. Stalk celery weight and vitamin C content were found to be reduced after the application of the potassium rate higher than 1.2 g K ∙ dm-3. The study found that the salt concentration in the medium increased with an increase in the rate of potassium and that there was no effect of the increased rate of calcium carbonate on total salt concentration in the medium of stalk celery. The different rates of calcium carbonate affected the uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, and magnesium by stalk celery.
References
Dzida K. 2004. Wpływ nawożenia azotowo potasowego na plonowanie buraka liściowego (Beta vulgaris var. cicla) i zawartość składników w podłożu. Rocz. AR Pozn. CCCLVI, Ogrod. 37: 55–60.
Dzida K., Jarosz Z. 2010. Effect of calcium carbonate and differentiated nitrogen fertilization upon the yield and chemical composition of spinach beet. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 9 (3): 201–210.
Golcz A. 1996. Skład chemiczny papryki w zależności od odmiany i stopnia dojrzałości owoców. VI Konferencja Katedr Uprawy Roli i Nawożenia Roślin Ogrodniczych Akademii Rolniczych „Nawożenie roślin ogrodniczych - stan badań i kierunki rozwoju” (20-21.06.1996 r., Kraków): 55–56.
Kowalska I. 2004. Zawartość wybranych składników w szpinaku (Spinacia oleraceae L.) uprawianym przy zróżnicowanej zawartości wapnia. Rocz. AR Pozn., CCCLX, Ogrod. 38: 105–110.
Li Y., Wang T., Li J., Ao Y. 2010. Effect of phosphorus on celery growth and nutrient uptake under different calcium and magnesium levels in substrate culture. Hort Sci. (Prague) 37: 99–108.
Isidora R., Pavlovic M., Sala F., Adina B. 2008. Potassium fertilization influence upon vegetables yield quality and soil fertility protection. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 40 (2): 147–152.
Lester G.E., Jifon J.J., Makus D.J. 2010. Impact of potassium nutrition on food quality of fruits and vegetables: A condensed and concise review of the literature. Better Crops 94 (1): 18–21.
Michałojć Z., Wołodko A., Nowak L. 2006. Wpływ nawożenia potasem na wzrost, kwitnienie, walory dekoracyjne i skład chemiczny celozji (Celosia argantea var. cristata L.). Acta Agroph. 7 (4): 983–990.
Nurzyński J. 2008. Nawożenie roślin ogrodniczych. Wydawnictwo AR w Lublinie, Lublin.
Perucka I., Materska M. 2004. Wpływ Ca2+ na zawartość witaminy C, prowitaminy A i ksantofili w owocach wybranych odmian papryki ostrej. Ann. UMCS Sect. E 59 (4): 1933–1939.
Pitura K., Michałojć Z., Nowak L. 2012. Wpływ rodzaju nawozu potasowego oraz dawki węglanu wapnia na stężenie soli w podłożu, plonowanie i wartość biologiczną wybranych gatunków roślin warzywnych. Annales UMCS, EEE Hort. XXII (3): 13–20.
PN -A-04019. 1998. Oznaczanie zawartości witaminy C. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny.
Pudelski T. 2002. Uprawa warzyw pod osłonami: 245–246. PWRiL, Warszawa.
Rumpel J. 2005. Uprawa selera korzeniowego, naciowego, listkowego. Hortpress, Warszawa.
Wińska-Krysiak M., Łata B. 2007. Wpływ zróżnicowanego nawożenia wapniem na plonowanie pomidora odmiany ‘Geronimo F1’ i linii DRW 7428 F1 (typ Cunero), uprawianych na wełnie mineralnej. Rocz. AR. Pozn. CCCLXXXIII, Ogrod. 41: 661–666.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.