Computer aided identification of the Ficus L. species by the lamina shape
Abstract
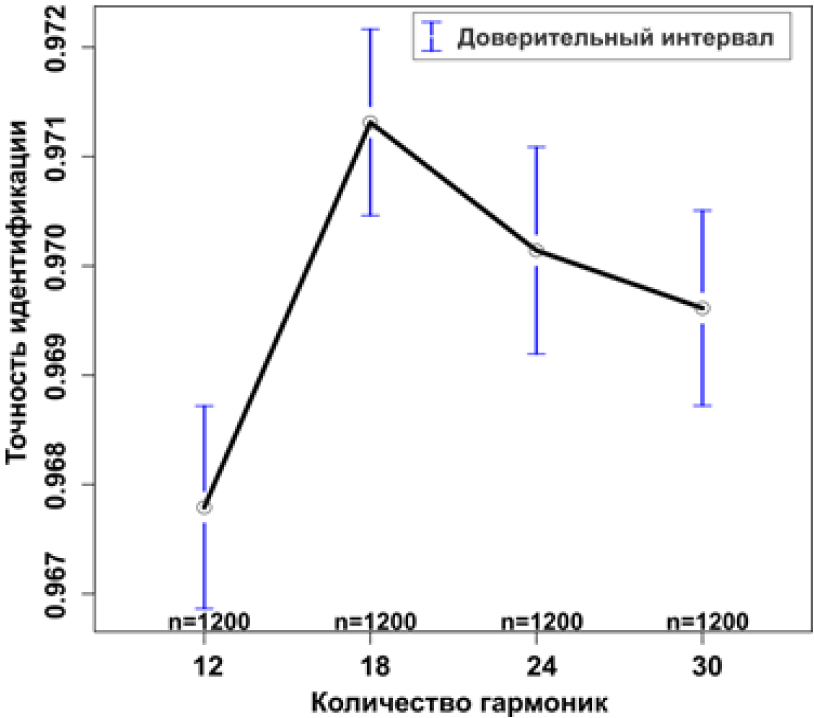
The development of computer aided plant species determination is the urgent task of the botanical science. Identification is often bases on the morphology of the lamina. It is promising to describe the leaf shapes through the harmonic values of elliptic Fourier decomposition, but the effectiveness of this approach requires further verification. Another task is a comparative evaluation of different classification algorithms. The work was conducted on the 2812 leaves images of the 15 Ficus L. species. To solve the described tasks the optimal set of the Fourier decomposition parameters was determined. The best results are achievable by using the classification with 18 Fourier harmonics. Number of reference points on the outline does not affect the result of the models. We compared an identification accuracy of the 30 classification algorithms. Random forest algorithm had the highest classification accuracy – 98%. Combining different prediction algorithms by stacking improves the efficiency of the leaf shapes recognition.
References
Breiman L., Friedman J., Olshen R., Stone C. 1984. Classification and regression trees. Wadsworth.
Claude J. 2008. Morphometrics with R. Springer, New York.
Friedman J. 1991. Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann. Stat. 19 (1): 1–141.
Friedman J.H. 2002. Stochastic gradient boosting. Comp. Stat. Data A. 38 (4): 367–378.
Hastie N. 2009. Elements of statisical learning – data mining, inference and prediction (2nd edition). Springer, New York.
Hothorn T., Lausen B., Benner A., Radespiel-Troger M. 2004. Bagging survival trees. Stat. Med. 23 (1): 77–91.
Kuhn M. 2008. Building predictive models in R using the caret package. J. Stat. Soft. 28 (5): 1–26.
Kumar N., Andreou A. 1998. Heteroscedastic discriminant analysis and reduced rank HMMs for improved speech recognition. Speech Commun. 25: 283–297.
Lee C.-L., Chen S.-Y. 2006. Classification of leaf. Int. J. Imaging Sys. Tech. 16 (1): 15–23.
Martens H., Næs T. 1989. Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chichester.
Menze B.H., Kelm B.M., Splitthoff D.N., Koethe U., Hamprecht F.A. 2011. On oblique random forests. ECML PKDD'11 Proceedings of the 2011 European conference on Machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases. Vol. 2: 453-469.
Neto J.C. 2006. Plant species identification using Elliptic Fourier leaf shape analysis. Comp. Electr. Agricult. 50 (2): 121–134.
Phatak A., Kiiveri H., Clemmensen L.H., Wilson W.J. 2010. Constructing dependency networks using sparse linear regression. Bioinformatics 26 (12): 1576–1577.
Press W.H., Flannery B.P., Teukolsky S.A., Vetterling W.T. 1992. Numerical recipes in C. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Quinlan R. 1993. Programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
R Core Team 2012. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/.
Schindelin J., Arganda-Carreras I., Frise E., Kaynig V., Longair M., Pietzsch T., Preibisch S., Rueden C., Saalfeld S., Schmid B., Tinevez J.Y., White D.J., Hartenstein V., Eliceiri K., Tomancak P., Cardona A. 2012. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 9: 676–682.
Simon N. 2011. Regularization paths for Cox's proportional hazards model via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Soft. 39 (5): 1–13
Singh K., Gupta I., Gupta S. 2010. SVM-BDT PNN and Fourier moment technique for classification of leaf shape. Int. J. Signal Process., Image Process. Pattern Recogn. 3 (4): 67–78.
Strobl C., Malley J., Tutz G. 2009. An introduction to recursive partitioning. Psy. Meth. 14 (4): 323–348.
Tibshirani R., Hastie T., Narasimhan B., Chu G. 1999 Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (10): 6567-6572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082099299
Venables W.N., Ripley B.D. 2002. Modern applied statistics with S. 4th edition. Springer.
Wang X.-F. 2005. Recognition of leaf images based on shape features using a hypersphere classifier. Adv. Intel. Computing. 364: 87–96.
Wolpert D. 1992. Stacked generalization. Neural Networks 5 (2): 241–259.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.